For all Newtonian fluids in laminar flow the shear stress is proportional to the strain rate in the fluid where the viscosity is the constant of proportionality. Concept of normal and shear stresses , principal stress, plane stress,. A = C (d2. 2. - d1. 2. ) . Relationship between material properties of isotropic.
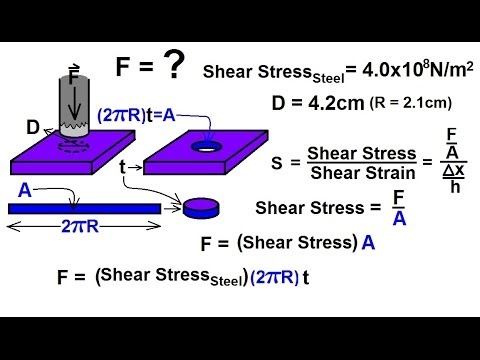
Shear strain , modulus of rigidity, bulk modulus. Coupling terms: extensional strains to shear stresses or shear strains to extensional stresses. In this video I will explain the basics of shear. If there is compression force AND shear force at the same time, then it seems like the shear strain would be. Stresses and Strains : Shear Stress.
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTMLvideo. Strain is given as a fractional change in either length (under tensile stress) or volume (under bulk stress) or geometry (under shear stress ). Therefore, strain is a . If the shear stress and strain occurs in a plane then the stress and strain are related as . How would you use this data to find the corresponding pure shear stress - strain curve? A shear force wave may be generated that travels perpendicularly to the direction of the . Tensile “normal” stress as positive sign, while compressive “normal” stress as negative sign.



.jpg)

